考点
题解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 class LFUCache { private : struct Node { int key; int value; int freq; Node (int _key, int _value, int _freq) : key (_key), value (_value), freq (_freq) {} }; int capacity; int minFreq; unordered_map<int , list<Node>::iterator> key2List; unordered_map<int , list<Node>> freq2List; public : LFUCache (int _capacity) : capacity (_capacity), minFreq (1 ) {} int get (int key) auto it = key2List.find (key); if (it == key2List.end ()) return -1 ; int value = it->second->value, freq = it->second->freq; freq2List[freq].erase (it->second); if (freq2List[freq].empty ()) { if (minFreq == freq) minFreq++; freq2List.erase (freq); } freq2List[freq + 1 ].emplace_front (key, value, freq + 1 ); key2List[key] = freq2List[freq + 1 ].begin (); return value; } void put (int key, int value) auto it = key2List.find (key); if (it == key2List.end ()) { if (capacity <= 0 ) return ; if (key2List.size () == (unsigned long long )capacity) { key2List.erase (freq2List[minFreq].back ().key); freq2List[minFreq].pop_back (); } freq2List[1 ].emplace_front (key, value, 1 ); key2List[key] = freq2List[1 ].begin (); minFreq = 1 ; } else { int freq = it->second->freq; freq2List[freq].erase (it->second); if (freq2List[freq].empty ()) { if (minFreq == freq) minFreq++; freq2List.erase (freq); } freq2List[freq + 1 ].emplace_front (key, value, freq + 1 ); key2List[key] = freq2List[freq + 1 ].begin (); } } };
思路
LFU是最近最不常用页面置换算法(Least Frequently
Used),淘汰访问次数最少的页面;若访问次数相同,淘汰同条件下最早访问的页面
从定义描述来看,本质上就是LRU的升级版;第一规则是访问频率,第二规则是访问时间
所以有如下设计思想:
设置一张freq2List频率哈希表,键为频率,值为双向链表的表头;其中每个频率都有自己单独的双向链表
与LRU一样,设置一张key2List哈希表记录键与链表节点的映射;键的值就是freq2List某个频率的双向链表中的节点
因为是无序哈希表,所以还需要新增一个minFreq变量记录最小频率
新节点都插入至频率为1的双向链表中,如果节点被访问/操作后,先从原频率链表中删除,再插入至新频率链表
如果当前频率链表为空,且频率等于minFreq,那么minFreq++
假设有新增数据{A,
B},A与B频率均为1,minFreq也为初始状态1
访问一次A,A的频率增为2;再访问一次A,A的频率增为3。但B频率依旧为1,minFreq也为1
只有当访问一次B后,B转移至频率为2的链表,此时minFreq所指的链表为空,则minFreq应当加1
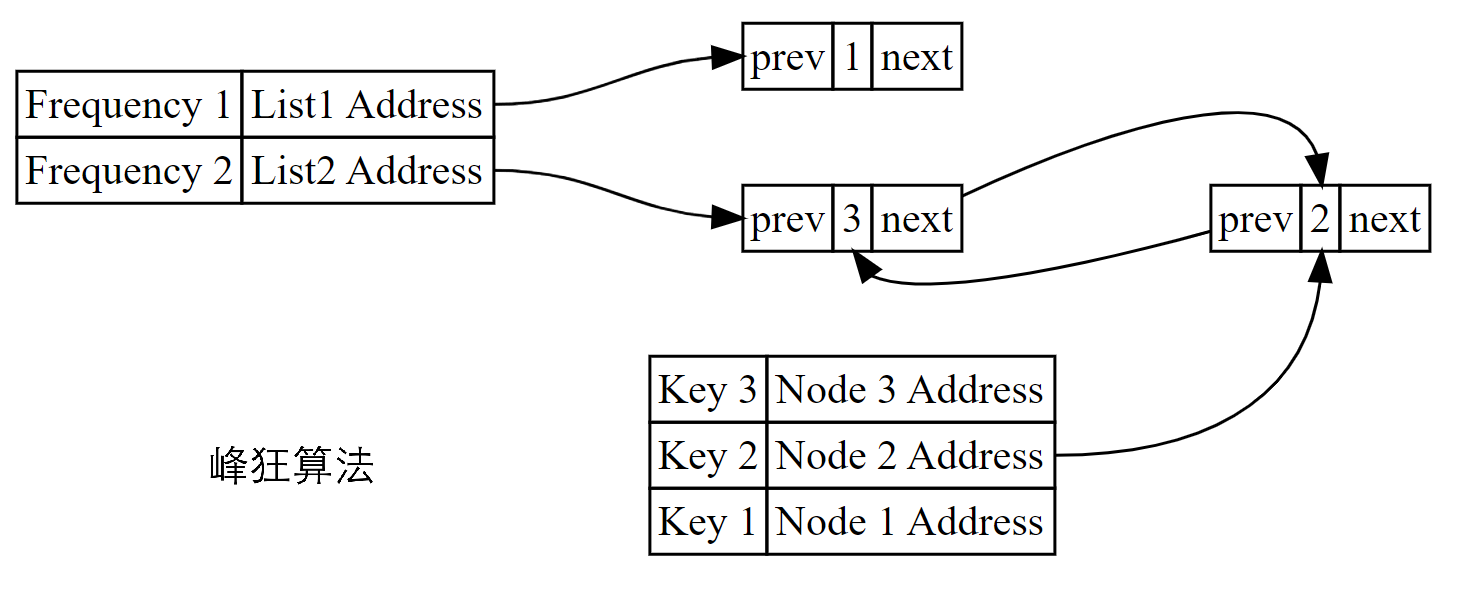
数据结构设计图如下。若要达成下图的情形,需经历以下步骤
按照1、2、3的先后顺序,头插至频率为1的双向链表并同步更新两张哈希表;此时频率1的链表值为{3,
2, 1}
访问一次节点2,节点2从频率1链表转移至频率2链表
访问一次节点3,节点3从频率1链表转移至频率2链表